How To Choose The Right Data Network For Your Smart Building Solution

By Matthew Walker, Smarter Technologies & NFC Group founder.
If you’re looking for a wireless solution to monitor, track, and control your smart building, it can be difficult to know which connectivity network and supplier to use. Each network has distinct features, benefits and limitations that determine the most appropriate use cases and rule out others.
If you’re interested in identifying the right network for your smart building, this article will be a valuable tool to help get you started. I’ve outlined the features, benefits, and applications of Smarter Technologies’ Orion Data Network and compared them to those of other network solutions.
What is the Orion Data Network?
Smarter Technologies’ proprietary Orion satellite data network is a military-grade, end-to-end, low frequency, long range radio solution. It combines RFID, GPS and IoT sensor technology to securely deliver your asset data in real time.
These attributes make the Orion Data Network the ideal solution for 360-degree smart building visibility and security. Our team of expert developers can also design, build, test, and deploy bespoke solutions to meet your building’s specific requirements.
But before we get ahead of ourselves, let’s give you the information you need to decide for yourself which network will work best for your requirements.
What should you look for in a network to find the right solution for your needs?
- Range
- Power consumption
- Positioning resolution (accuracy / latency)
- Data transmission rate
- Packet size
- Compatible hardware
- Security by design
- Regulatory compliance
- Scalability
- Overall cost (device, deployment, maintenance)
- Business applications
- Business outcomes
- CapEx and OpEx reduction / ROI
What are some of the other data networks out there?
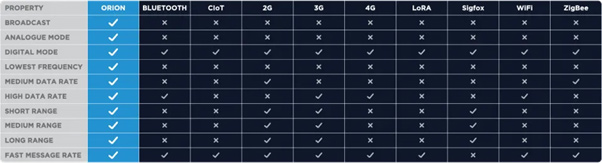
Zigbee
Zigbee is a low-power, low data rate, short range (2.4GHz radio band globally with 868MHz option in Europe), close proximity wireless personal area network. It has a defined data rate of 250 kbit/s utilised for intermittent data transmissions. It’s ideal for smart home devices such as the Amazon Echo and Philips Hue bulb. Zigbee users benefit from the long battery life. It is also generally more cost-effective than Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a low-power, low-cost option that supports large-scale deployments. It’s frequently used for products that enable you to listen to music while near your phone or to connect your phone to your car. However, the range is small, and there is the potential for interference from other signals on the same frequency spectrum.
Sigfox
Sigfox is a global long-range wireless network that connects low-power objects like smartwatches and electricity meters, which need to be “always-on” and only transfer small amounts of data. It has a low data rate of 10 - 1000bps and operates in the 900MHz band, and it is not appropriate for large deployments or assets transmitting a lot of data.
LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN is a long-range wide area network that uses sub-GHz ISM bands to penetrate the core of large structures and substructure deployments. The functionality is similar to Sigfox, but it uses encoded packets to transmit information across various frequency channels instead of utilising narrowband transmission. It’s unsuitable for large data payloads and is not applicable for continuous monitoring or real-time applications requiring lower latency.
GSM
GSM or 2G is the most widely used cellular-wireless telecommunications standard used by mobile phone carriers like EE and Virgin Mobile. It offers long-range and good security protection. It was the standard for Machine to Machine (M2M) SIMs but, with the arrival of 4G and advancing applications of 5G, it’s no longer the most cost-effective or reliable option. Users are suffering from the global remapping and resultant gaps in the network. If your IoT items rely on 2G, you need to be implementing your strategy to swap your devices to another network.
How does Orion stack up?
The Orion Data Network uses active RFID tags because this gives our sensors their own power source and enables us to transmit your information over a greater range. The ability to utilise different Mhz means we can transmit a lot more data than many competitors while remaining compliant with regulations, and (perhaps the most beneficial feature) your data is delivered to you in real time.
Our range of smart sensors allows you to monitor your electricity, gas and water usage to understand your consumption profile, cut waste and manage sustainability reporting. Our smart building solution also covers air quality, humidity, temperature as well as waste monitoring to ensure your buildings can be managed and maintained to the highest level with maximum efficiency. SmarterView is the official dashboard for the Orion Network and property of Smarter Technologies Group. This platform is purpose-built for smart building management and comes standard with any Orion Data Network installation.
Orion benefits overview
- Real-time data transmission
- Cost-effective
- Wireless
- SIM-free
- Coverage ranging from 1 to 15 kilometres
- Easily scaled up or down
- 3-year battery life
- End-to-end system, quick to set up and integrate
- Signal penetrates walls, metal, and underground
- Anti-jamming technology
- Hand-held Beacon recovery mode
- Military-grade security / encrypted data
- Heat mapping technology
- Can help reduce your carbon footprint
Sound like the right solution for your smart building?
Get in touch with the Smarter Technologies team to learn more.
Wireless Network Comparison Table